The project’s main idea is to establish a recycling and processing plant for used car, engine, and generator oils. The plant collects used oils and passes them through manufacturing processes including filtration, hydrogenation, blending, and refining to convert them back into usable oils. The plant’s products include “recycled oils,” which are divided into: (gasoline engine oils – refined oils – hydraulic engine oils – diesel engine oils). The final product is the produced oils, which are divided into: (light base oil 150 SN – medium base oil 300 SN – heavy base oil 500 S).

mashroo3k Company for Economic and Management Consulting is preparing a feasibility study for an oil recycling plant project. After reviewing all the project’s marketing axes, we discovered a pressing need for the project’s products, namely recycled oils, which are divided into (gasoline engine oil, refined oils, hydraulic engine oils, and diesel engine oils). As a result, demand for the project’s products will increase, which are divided into (150 SN light base oil, 300 SN medium base oil, and 500 S heavy base oil). The marketing study revealed the market’s need for such products. <br>The project is considered a green concept that benefits environmental protection, as the plant recycles waste oils that cause environmental pollution, making them available for reuse. It’s worth noting that the plant will offer its products using the best and most modern technologies. These products will be of high quality and competitively priced, suitable for all target groups and sectors. This will enable the project to capture a significant portion of the marketing gap, benefiting from the growing demand for its products.



Executive summary
Study project services/products
Market Size Analysis
Risk Assessment
Technical study
Financial study
Organizational and administrative study
The technological advancement witnessed by the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries—along with population growth—has led to an increase in waste generated from both human and industrial activities. This surge in waste has posed a significant challenge to GCC governments, urging them to address the issue swiftly to avoid environmental and health risks.
The total amount of waste generated in the GCC (both hazardous and non-hazardous) is estimated at approximately 131.8 million tons, with hazardous waste accounting for 1.2%, and non-hazardous waste making up 98.8%.
Mashroo3k Economic and Administrative Consulting presents the following key indicators for the recycling sector in the GCC:
Total hazardous waste collected in the GCC: 1.6 million tons.
Total non-hazardous waste collected: 130.2 million tons.
Hazardous waste is divided as follows:
6% medical waste
81.8% industrial waste
12.2% other types (e.g., batteries and electronic waste)
Non-hazardous waste is divided as follows:
40.7% construction waste
25% household waste
1.7% green waste
32.5% other types
51% (67.2 million tons) of total collected waste is treated.
Industrial waste collected in the GCC totals 1.3 million tons, with Saudi Arabia and the UAE accounting for 63.1% and 19.3% respectively of that amount.
Household non-hazardous waste collected in the GCC amounts to 32 million tons.
The UAE ranks first in the amount of waste recycled, with a share of 42.8%.
100,000 tons of hazardous waste (or 9.3%) is recycled.
Saudi Arabia leads in solid waste volume, generating over 16 million tons annually, followed by the UAE with 5.4 million tons.
Food and green waste: 58%
Glass: 3%
Metals: 3%
Paper and cardboard: 13%
Plastic: 12%
Wood: 1%
Rubber and leather: 2%
Other waste: 8%
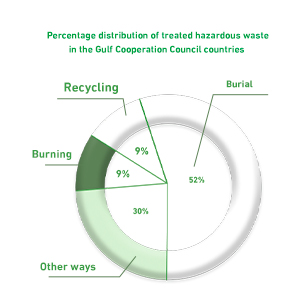
Hazardous Waste:
Incineration: 9%
Landfilling: 51.7%
Recycling: 9.3%
Other methods: 30%
Non-Hazardous Waste:
Landfilling: 51%
Other methods (e.g., incineration, recycling): 49%
Reducing primary energy consumption by about 4%
Creating 50,000 jobs in the recycling sector
Cutting CO₂ emissions by 13 million tons annually
Contributing $138 billion USD to GCC economies between 2020 and 2030
Mashroo3k recommends investing in the recycling sector for the following reasons:
The world produces approximately 2.01 billion tons of municipal solid waste annually, expected to rise to 3.40 billion tons by 2050.
In 2014, the global output of electronic waste reached 12.8 million metric tons, increasing to 53.6 million metric tons by 2019.
Plastic and paper account for around 29% of total global waste, making them promising sectors for profitable recycling investment.
Mashroo3k Economic Consulting affirms that the volume of waste in Saudi Arabia now exceeds 45 million tons annually. With the Kingdom’s commitment to raising the recycling rate from 1% to 80% by 2035, the company sees investment in this vital sector as highly profitable. Regarding the future of recycling and energy generation, the following prospects can be highlighted:
In Saudi Arabia, 45,000 terajoules of energy could be saved annually just by recycling glass and metals.
An estimated 3 terawatt-hours of electricity could be generated every year by utilizing all food waste through biogas facilities in the Kingdom.
Additionally, 1 to 1.6 terawatt-hours of electricity per year could be produced by processing plastic and other mixed waste—such as paper, cardboard, wood, textiles, leather, etc.—using pyrolysis technologies.
Mashroo3k emphasizes that recycling is one of the most promising sectors in the Kingdom, and projects in this area represent genuine investment opportunities, especially as Saudi Arabia moves toward a green economy. Environmental protection has become a key priority for the country’s leadership, clearly reflected in Vision 2030.
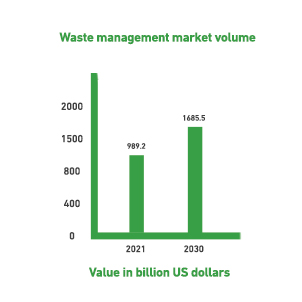
The global waste management market was valued at approximately USD 989.20 billion in 2021, and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2022 to 2030, reaching USD 1,685.5 billion by the end of the forecast period.
The Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region is expected to experience a CAGR of 6.3% in recycling and waste management between 2022 and 2030. This growth is driven by increased awareness of the sustainable benefits of waste reuse and recycling.